
Trenching and Excavation Fatalities Reach Alarming Number

Written by: Joe Mangiardi, NES, Inc.
 Trenching and excavation fatalities have hit a high in recent years; the above safety poster can be downloaded here.
Trenching and excavation fatalities have hit a high in recent years; the above safety poster can be downloaded here.
Trenching and Excavation Fatalities on the Rise
Following a recent upward trend in the rate of trenching and excavation fatalities, this month federal OSHA promulgated a trade release updating its National Emphasis Program (NEP) on preventing trenching and excavation collapses. The publication indicates that the NEP will be making a concerted effort to ramp up education and enforcement regarding trenching and excavation safety. Loren Sweatt, Deputy Assistant Secretary of Labor for Occupational Safety and Health, states in the trade release that “Removing workers from and helping workers identify trenching hazards is critical. OSHA will concentrate the full force of enforcement and compliance assistance resources to help ensure that employers are addressing these serious hazards.”
Trenching and excavation inspections will also be recorded in a national reporting system, and trenching and excavation hazards outreach programs are set to be developed by OSHA offices nationwide. As with all federal compliance programs, individual states will be required to enforce regulations that are at least as stringent.
The NEP outreach efforts are set to be most intensively implemented during the last three months of 2018, during which time “OSHA will continue to respond to complaints, referrals, hospitalizations, and fatalities. Enforcement activities will begin after the outreach period and remain in effect until canceled.”
The hope will be that future labor statistics will reflect a downward trend in trenching and excavation fatalities. Currently, those statistics (as reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics) show that there were 36 excavation or trenching cave-in deaths across all U.S. industries in 2016, a number that nearly equals those figures for the previous two years combined. As would be expected, the vast majority of these incidents occur in the construction industry.
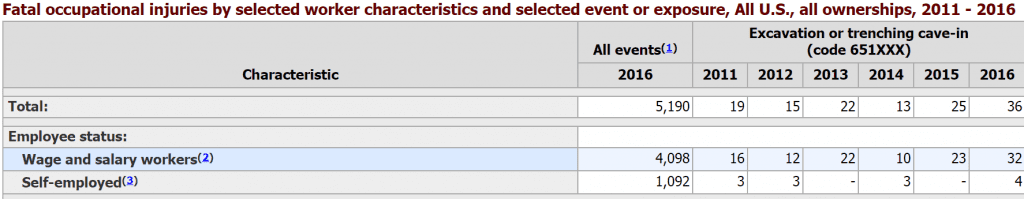 The above report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics shows 2016 as having the highest rate of trenching and excavation fatalities in the available range of 2011-2016.
The above report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics shows 2016 as having the highest rate of trenching and excavation fatalities in the available range of 2011-2016.
For more information on trench safety, including a summary of NIOSH recommendations, refer to the June 2018 NES article 2018 Trench Safety Stand-Down.
Trenching and Excavation Regulations
This section will outline key elements of the Cal/OSHA statutes, Title 8 California Code of Regulations (8 CCR) 1539-1541.
Federal regulations applicable to trenching and excavation operations are located in Title 29 of the Code of Federal Regulations (29 CFR) 1926.650-652.
Title 8 CCR 1539 defers to 8 CCR Chapter 3.2, Article 2, Section 341 for guidance on trenching and excavation permits, which must be obtained prior to work being started on any permit-required activities. Provided that the holder of the Project Permit functions as Project Administrator for the duration of the project, only one Project Permit per project is necessary. Any employer working the project other than this Project Permit holder must maintain an Annual Permit. These permits are required for the “construction of trenches or excavations 5 feet or deeper into which any person is required to descend.” Exemptions apply in the cases of:
- Emergency repair work in underground facilities
- Construction or final use of excavations or trenches for which no worker will be descending into the excavation or trench
- Gravedigging
- Swimming pool construction
In 8 CCR 1540 excavation-related definitions are provided (trenches are classified as excavations). Key definitions include:
- Benching or Benching System: method of protecting employees from cave-ins by forming horizontal levels or steps
- Excavation: any man-made cut, cavity, trench, or depression in an earth surface formed by earth removal
- Faces or Sides: vertical or inclined earth surfaces formed as a result of excavation work
- Hazardous Atmosphere: an atmosphere that may cause death, illness, or injury due to being explosive, flammable, poisonous, corrosive, oxidizing, irritating, oxygen-deficient, toxic, or otherwise harmful
- Protective System: support systems, sloping and benching systems, shield systems, and other systems that provide the necessary protection from cave-ins, rocks/soil/etc., or the collapse of adjacent structures
- Shoring or Shoring System: structure designed to prevent cave-ins such as a metal hydraulic, mechanical, or timber shoring system
- Sloping or Sloping System: method of excavating to form sides of an excavation that are inclined away from the excavation
- Trench or Trench Excavation: narrow excavation (in relation to its length) made below the surface of the ground; depth is typically greater than width, but the width of a trench (measured at the bottom) is not greater than 15 feet (after accounting for any forms or other structures that may reduce the dimensions)
General requirements are described in 8 CCR 1541. Protective system requirements are broken down in a subsection within this section that includes six appendices, A-F, which outline pertinent specifications regarding soil classification, sloping and benching, timber shoring for trenches, aluminum hydraulic shoring for trenches, alternatives to timber shoring, and excavations 20 feet or less in depth, respectively. Some important trenching and excavation general requirements include:
- Excavation is not to begin until the excavation area has been properly marked, locations of subsurface installations have been identified by a qualified person, the go-ahead has been received from the operators of such subsurface installations, and employees who will be involved in the operation have been trained in all applicable areas
- Subsurface installations must be protected or relocated as necessary, and any and all damages incurred during operations must be reported immediately
- Structural ramps used only by employees to enter or exit the excavation are to be designed by a competent person, and those constructed for use by equipment are to be designed by a competent person qualified in structural design
- Any trench excavation of more than 4 feet in depth is to have a stairway, ladder, ramp, or other safe means of egress that requires a maximum of 25 feet of lateral travel
- If employees will be exposed to public vehicular traffic, they are to be provided with, and required to wear, warning vests or other such reflective or high-visibility garments
- Employees are not allowed underneath loads handled by lifting or digging equipment
- Mobile equipment is to have an adequate warning system
- Excavations greater than 4 feet in depth shall be tested and controlled to ensure employees are not exposed to any hazardous atmospheres (oxygen-deficient or oxygen-enriched); this includes providing ventilation and/or respiratory protection equipment
- Emergency rescue equipment is to be available, used when required, and attended when in use
- Employees are not to work in excavations in which water has accumulated or is accumulating unless adequate engineering measures have been implemented
- If adjacent structures of any kind are threatened by excavation operations, including when excavating below the base or footing of any foundation or retaining wall, support systems (shoring, bracing, underpinning, etc.) are to be utilized (subject to the discretion of a registered professional engineer)
- Workers must be adequately protected from falling, shifting, or rolling rocks, soil, or other materials or equipment
- Excavation(s), their adjacent areas, and protective systems must be inspected by a competent person prior to the start of work, after every rain storm, whenever a new potential hazard is introduced to the site, and as needed throughout the shift; employees are to be immediately removed from the excavation(s) when any hazards are identified
- Walkways/bridges with standard guardrails must be provided wherever employees or equipment will be crossing over excavations more than 6 feet in depth and 30 inches in width
- All wells, pits, shafts, etc., shall be barricaded or covered during operations and adequately backfilled when the operations have been completed
Employers are encouraged to consult the regulations in greater detail for the full scope of requirements.
Federal OSHA has released various new resources to assist in spreading the word on trenching and excavation safety. These include a poster, sticker, and QuickCard and can be found on OSHA’s trenching and excavation webpage.
 These OSHA trenching safety QuickCards in English and Spanish can be downloaded from federal OSHA’s trenching and excavation webpage.
These OSHA trenching safety QuickCards in English and Spanish can be downloaded from federal OSHA’s trenching and excavation webpage.
NES Trenching and Excavation Training
Trenching and excavation fatalities are preventable with proper training and the diligent implementation of applicable safety measures. NES regularly provides site-specific Trenching and Excavation Safety and Confined Space Operations training on behalf of public and private entities and their operations. For more information or to schedule on-site training for your employees, please call NES as 916-353-2360 / 800-637-2384 or email us at office@nesglobal.net.
References:
OSHA Trade Release: U.S. Department of Labor Updates National Emphasis Program on Trenching and Excavation Safety
8 CCR Chapter 3.2, Article 2, Section 341
OSHA Information Webpage: Trenching and Excavation
